 To determine whether Wnt/β-catenin-dependent reprogramming of fused cells is a mechanism of regeneration in higher vertebrates
To determine whether Wnt/β-catenin-dependent reprogramming of fused cells is a mechanism of regeneration in higher vertebrates
We will determine whether Wnt/β-catenin signalling controls in-vivo reprogramming of hybrids formed in response to injury. We will transplant perturbed (Wnt-activated or repressed) adult stem cells into a variety of drug-induced or genetically modified damaged organs. Short-term and long-term regeneration will be studied. Genetic approaches will be used to evaluate cell fusion, reprogramming and regeneration in the tissues analysed.
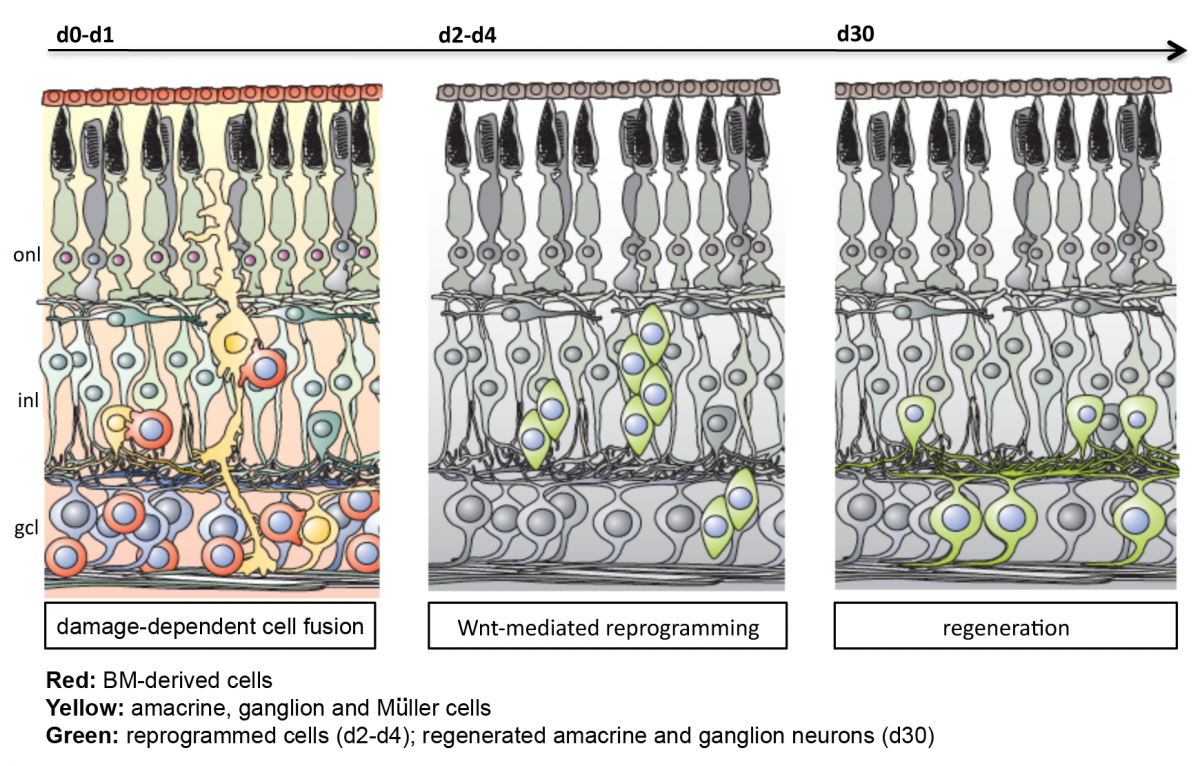
Figure above: Cell fusion mediated regeneration of retinal neurons. Taken from Sanges et al. Cell Reports 2013
